Managed Futures in Traditional Finance vs. SMAs in Digital Assets

In the ever-evolving world of investing, two strategies stand out for their unique approaches to portfolio diversification and professional management: Managed Futures in traditional finance and Separately Managed Accounts (SMAs) in the digital assets or cryptocurrency space. While both offer tailored solutions managed by experts, they cater to different markets, employ distinct mechanisms, and appeal to investors with varying goals. In this blog, we’ll break down what these strategies are, how they work, and how they differ—complete with examples to bring the concepts to life.
What Are Managed Futures in Traditional Finance?
Managed Futures refer to an alternative investment strategy where professional managers, known as Commodity Trading Advisors (CTAs), actively trade futures contracts on behalf of investors. These contracts are agreements to buy or sell assets—like commodities (gold, oil, wheat), currencies (USD, EUR), or financial indices (S&P 500 futures)—at a predetermined price and date in the future. Managed Futures have been a staple in traditional finance for decades, regulated in the U.S. by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) and the National Futures Association (NFA).
How Do They Work?
CTAs typically use a mix of algorithmic and discretionary trading strategies, with a strong emphasis on trend-following. This means they aim to capitalize on sustained price movements—up or down—in highly liquid futures markets. Investors open individual accounts with a CTA, who then trades on their behalf, often leveraging the account to amplify returns (and risks).
Key Features:
- Diversification: Managed Futures often have low or negative correlation with stocks and bonds, making them a hedge during market downturns.
- Liquidity: Futures contracts settle daily on regulated exchanges like the CME Group, ensuring transparency and easy access to funds.
- Flexibility: CTAs can go long (bet on rising prices) or short (bet on falling prices), profiting in both bull and bear markets.
Example:
Imagine an investor, Sarah, who allocates $100,000 to a Managed Futures account in 2025. Her CTA identifies a strong upward trend in crude oil prices due to geopolitical tensions. The CTA buys oil futures contracts, leveraging Sarah’s account to control $300,000 worth of oil. If oil prices rise 10%, Sarah’s account could see a $30,000 gain—tripling her initial return thanks to leverage. However, if prices drop, losses could also magnify.
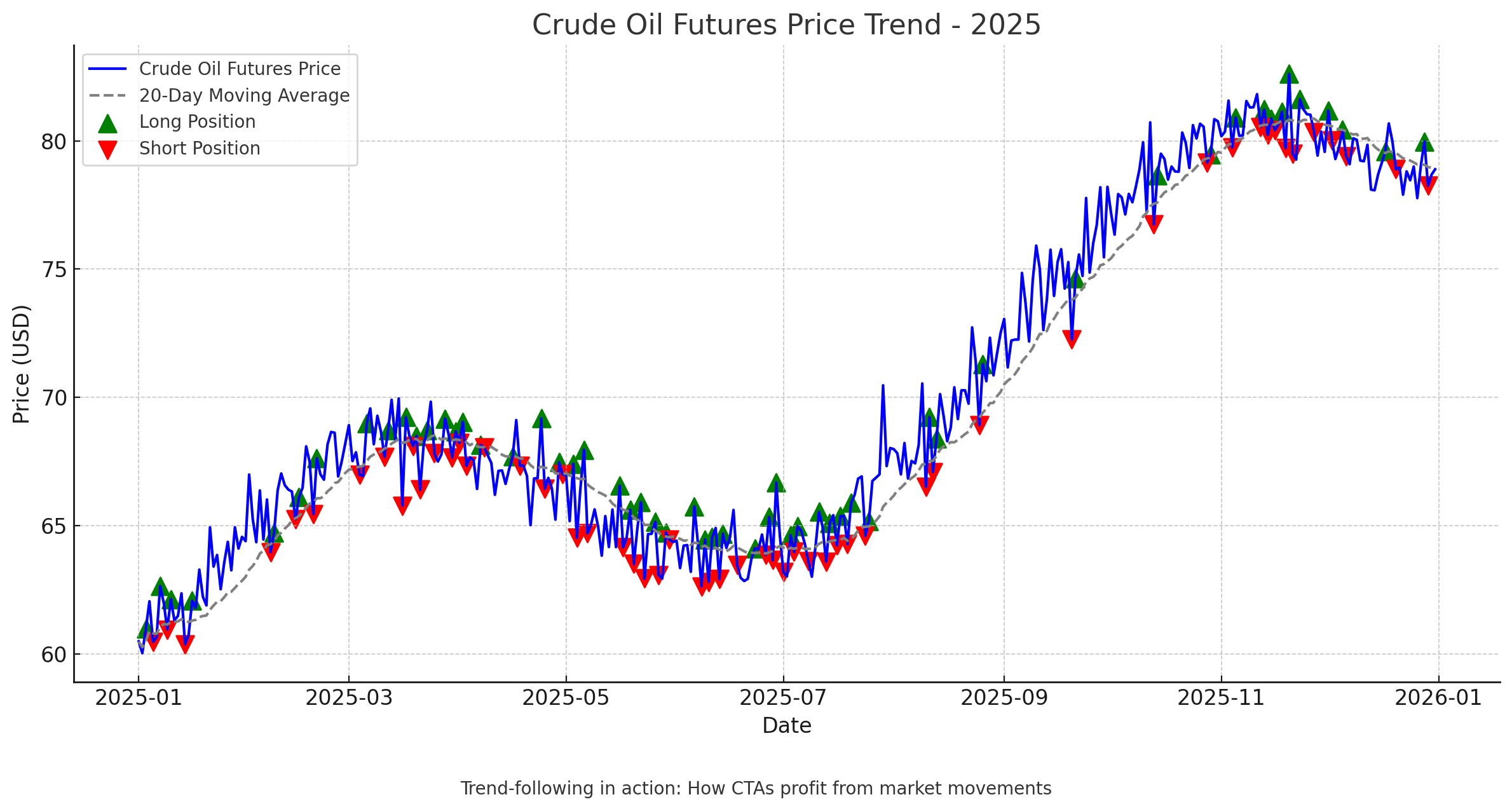
What Are SMAs in Digital Assets or Crypto?
A Separately Managed Account (SMA) in the crypto space is a personalized investment portfolio of digital assets—like Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), or altcoins—managed by a professional on behalf of a single investor. Unlike pooled funds (e.g., crypto ETFs), SMAs give the investor direct ownership of their assets, offering customization and transparency. This concept, borrowed from traditional finance, is gaining traction in the volatile, fast-paced crypto market.
How Do They Work?
An investor partners with a crypto asset management firm to set up an SMA. After discussing goals (e.g., long-term growth, income generation) and risk tolerance, the manager crafts a bespoke strategy. The manager then actively trades or holds digital assets in the investor’s account, often held in a secure wallet or with a custodian like Coinbase Custody, Copper or Ceffu
Key Features:
- Customization: SMAs can be tailored to an investor’s preferences—e.g., focusing on DeFi tokens or avoiding speculative altcoins.
- Transparency: Investors see exactly what they own (e.g., 2 BTC, 10 ETH) and can track performance in real time.
- Tax Efficiency: Direct ownership allows for strategic selling to harvest losses or gains, optimizing tax outcomes.
Example:
Consider Alex, who invests $50,000 in a crypto SMA in March 2025. His manager, aware of Alex’s moderate risk tolerance, allocates 45% to Bitcoin, 35% to Ethereum, and 20% to a stablecoin like USDC for stability. When Bitcoin surges 20% after a halving event, the manager locks in profits by selling a portion, then reinvests in Ethereum during a dip. Alex’s portfolio grows to $60,000, and he can withdraw his assets anytime since they’re in his name.
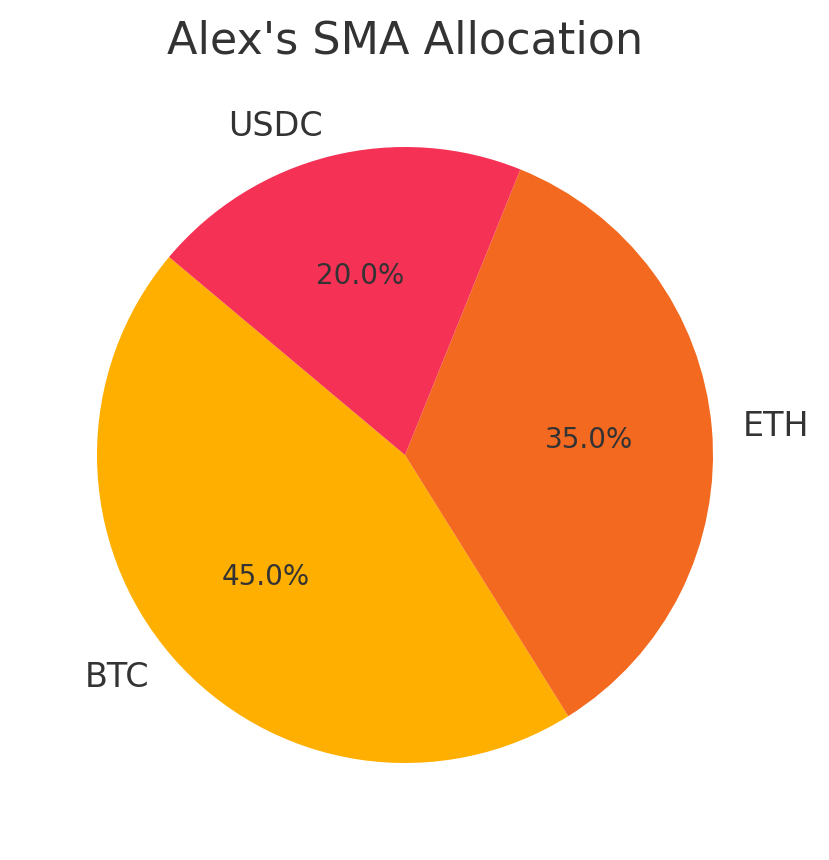
Comparing Managed Futures and Crypto SMAs
While both strategies involve professional management and aim to diversify portfolios, their differences are stark. Let’s break it down:
| Aspect | Managed Futures (Traditional Finance) | SMAs (Digital Assets/Crypto) |
|---|---|---|
| Asset Class | Futures contracts (commodities, indices, currencies) | Cryptocurrencies (BTC, ETH, altcoins) |
| Market | Regulated exchanges (e.g., CME, Eurex) | Crypto exchanges or wallets (e.g., Binance) |
| Strategy | Trend-following, long/short positions | Custom strategies (growth, income, hedging) |
| Ownership | Investor owns the account, not the underlying assets | Direct ownership of digital assets |
| Liquidity | High (daily settlement) | Varies (depends on exchange or wallet) |
| Risk | Leverage amplifies gains/losses | High volatility of crypto markets |
| Regulation | Heavily regulated by CFTC/NFA | Lightly regulated, varies by jurisdiction |
Real-World Context:
- Managed Futures: During the 2008 financial crisis, Managed Futures funds often posted positive returns as stocks and bonds tanked, thanks to their ability to short markets. In 2025, they might shine again if inflation drives commodity prices higher.
- Crypto SMAs: In 2021, Bitcoin’s rally to $69,000 rewarded SMA investors who held through volatility. In 2025, a manager might pivot to staking ETH for yield if market conditions stabilize.
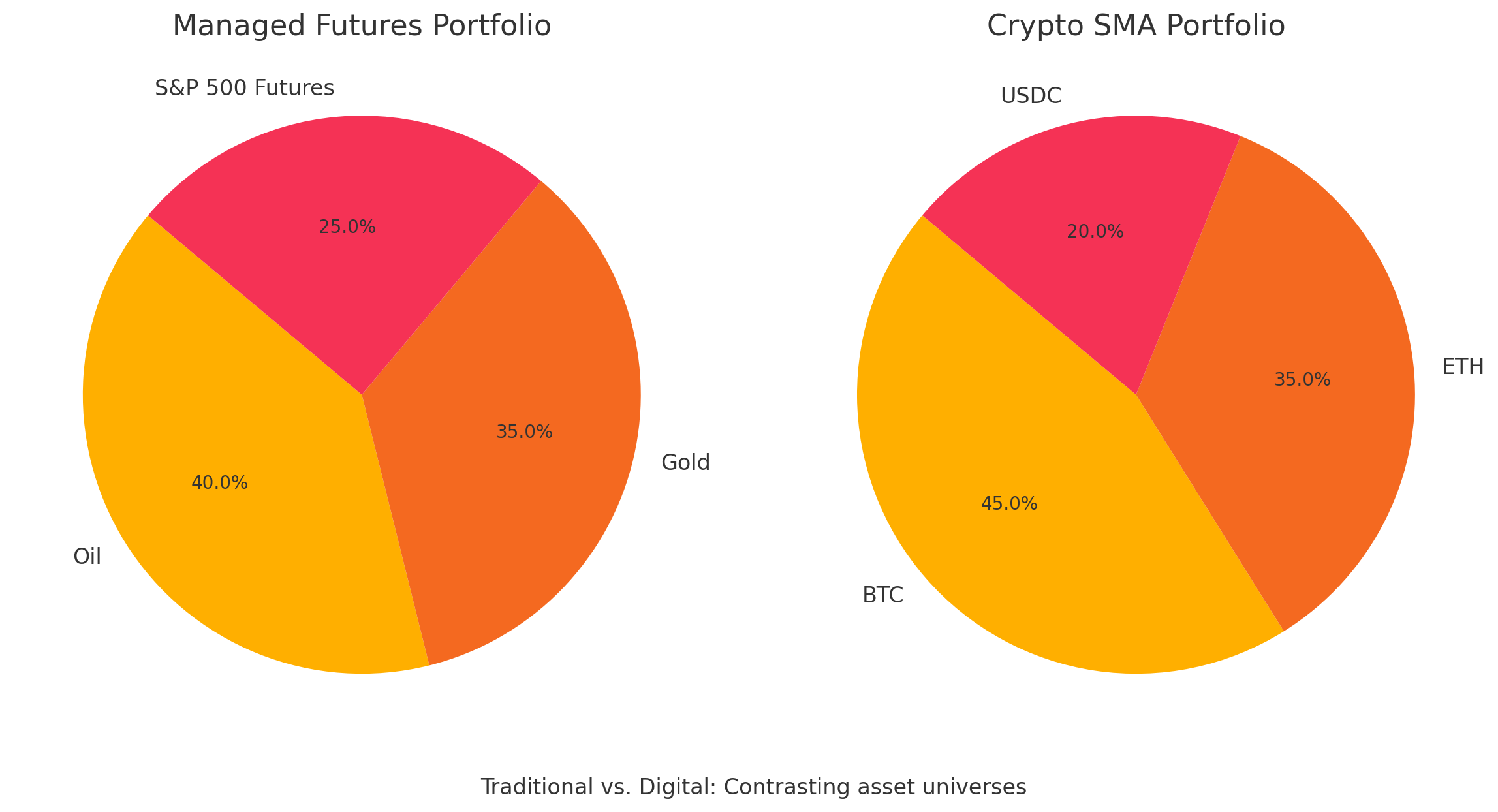
Pros and Cons
Managed Futures
- Pros: Proven track record, diversification benefits, regulated environment.
- Cons: High fees (e.g., 2% management, 20% performance), dependence on clear trends, leverage risks.
Crypto SMAs
- Pros: High growth potential, customization, direct asset control.
- Cons: Crypto volatility, regulatory uncertainty, higher minimum investments (often $50K+).
Which Is Right for You?
- Choose Managed Futures if you’re a traditional investor seeking a hedge against stock market downturns or inflation, with a preference for regulated, liquid markets.
- Choose a Crypto SMA if you’re bullish on digital assets, value personalization, and are comfortable with the Wild West of crypto volatility.
Both strategies offer unique ways to diversify, but they cater to different risk appetites and market outlooks. For a deeper dive into Managed Futures, check out Investopedia’s guide. For Crypto SMAs, explore Coinrule’s explanation.
Conclusion
Managed Futures and Crypto SMAs represent two sides of the investment coin: one rooted in the structured world of traditional finance, the other thriving in the dynamic realm of digital assets. Whether you’re chasing trends in oil futures or curating a Bitcoin-heavy portfolio, both approaches leverage expert management to unlock opportunities. As of March 16, 2025, with markets in flux, understanding these options could be your key to smarter investing.